16 November 2023
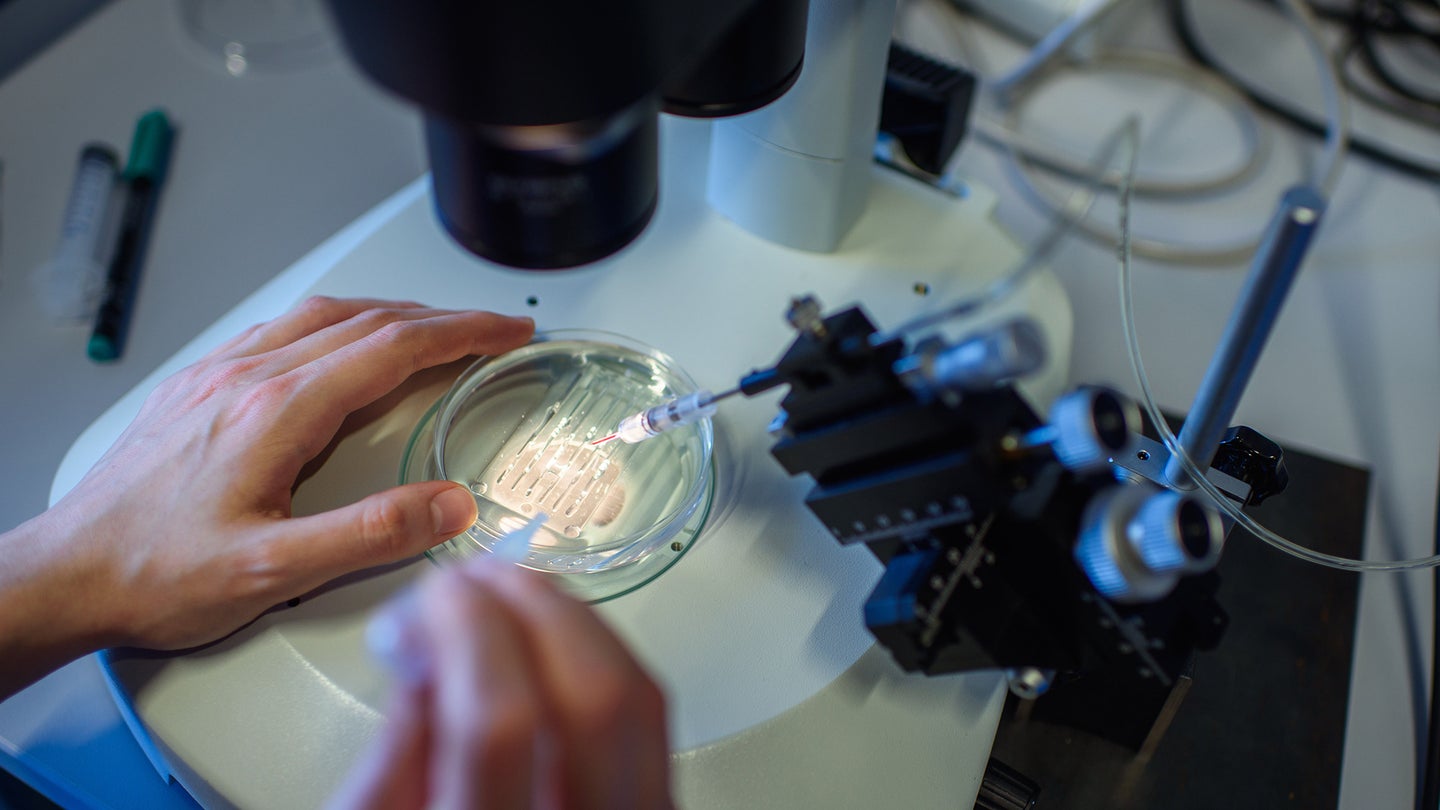
Casgevy relies on the gene-editing tool CRISPR, the developers of which won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2020.
Sickle-cell disease and β-thalassaemia are caused by errors in the DNA sequence of genes that encode for haemoglobin, a molecule that helps red blood cells to carry oxygen around the body.
In sickle-cell disease, abnormal haemoglobin makes blood cells misshapen and sticky, causing them to form clumps that can clog blood vessels. These blockages reduce the oxygen supply to tissues, which can cause periods of severe pain, known as pain crises.
β-thalassaemia occurs when mutations in the haemoglobin gene lead to deficient or absent levels of the oxygen-carrying molecule in red blood cells, low numbers of red blood cells and symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath and irregular heartbeats.
Clinicians administer Casgevy by taking blood-producing stem cells out of the bone marrow of people with either disease and using CRISPR to edit genes encoding for haemoglobin in these cells. The gene-editing tool an RNA molecule that guides the enzyme to the correct region of DNA and a Cas9 enzyme that cuts DNA.
Once the Cas9 enzyme reaches the gene targeted by Casgevy, called BCL11A, it cuts both DNA strands. BCL11A usually prevents the production of a form of haemoglobin that is made only in fetuses. By disrupting the BCL11A gene, Casgevy unleashes the production of fetal haemoglobin, which does not carry the same abnormalities as adult haemoglobin in people with sickle cell or β-thalassaemia patients.
Before the gene-edited cells are infused back into the body, people must undergo a treatment that prepares the bone marrow to receive the edited cells. Once administered, the stem cells give rise to red blood cells containing fetal haemoglobin. After some time, this relieves symptoms by boosting the oxygen supply to tissues. “Patients may need to spend at least a month in a hospital facility while the treated cells take up residence in the bone marrow and start to make red blood cells with the stable form of haemoglobin,” the MHRA said in a press release.
-
Tags
#DNA